Background
As organizations deploy large language models in production, hardware costs become a significant consideration. NVIDIA GPUs, while performant, represent a substantial investment. We were interested in evaluating whether Intel Arc Pro B60 could serve as a viable alternative for inference workloads.
The B60 offers specifications that warrant investigation:
- 24GB VRAM - sufficient for 30B parameter models
- 456 GB/s memory bandwidth
- 160 XMX engines for matrix operations
- Compatibility with established inference frameworks
This report documents our benchmarking methodology and findings.
Test Configuration
We would like to acknowledge Sparkle for providing the test hardware - a 4x Intel Arc Pro B60 workstation. This configuration allowed us to test with tensor parallelism (TP=4), which is representative of production deployments for models of this size.
Hardware
| Component | Specification |
|---|---|
| GPU | 4x Intel Arc Pro B60 |
| VRAM per GPU | 24GB |
| Memory Bandwidth | 456 GB/s per GPU |
| Tensor Parallelism | 4 (across all 4 GPUs) |
Software
We tested two configurations:
- vLLM 0.12: Built from source following the official documentation, packaged as a Docker image
- LLM-Scaler 1.2: An Intel-optimized build of vLLM, also distributed as a Docker image. This is not a different engine, but rather vLLM with Intel-specific optimizations.
Both configurations used Qwen/Qwen3-VL-30B-A3B-Instruct as the test model.
Workloads Evaluated
We selected workload patterns that represent common production scenarios:
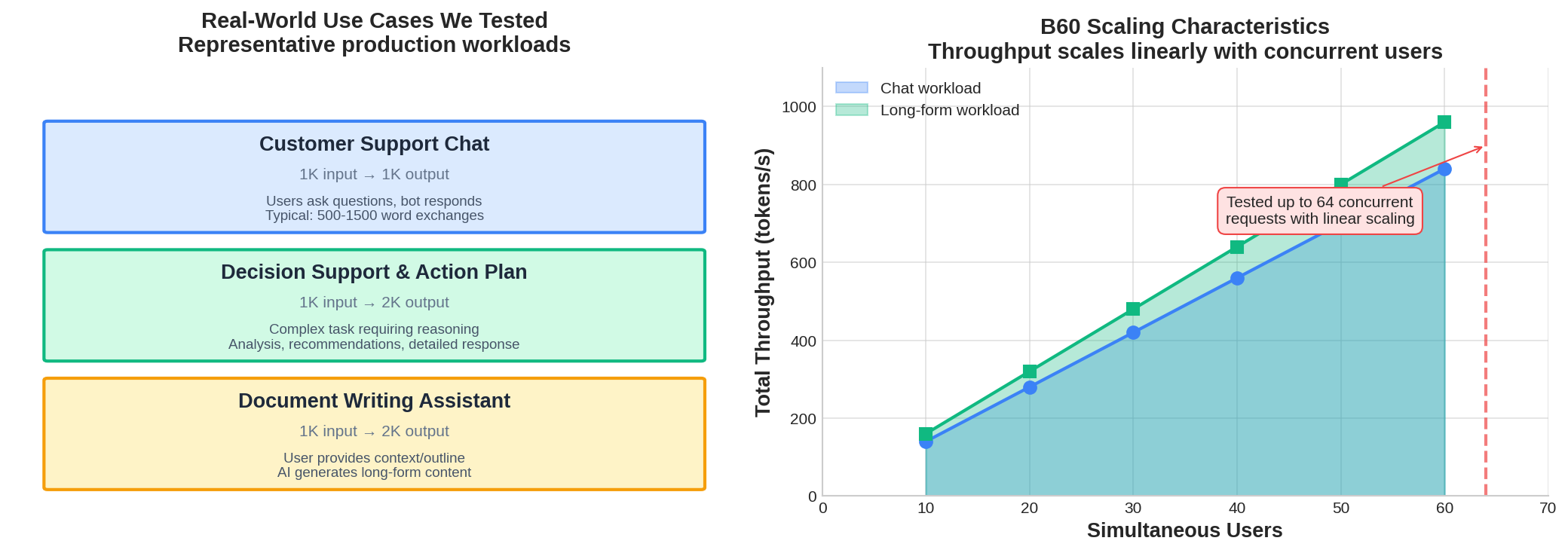 Figure 1: Test scenarios (left) and B60 scaling characteristics (right)
Figure 1: Test scenarios (left) and B60 scaling characteristics (right)
Scenario Descriptions
Customer Support Chat (1K → 1K): Short-form conversational interactions where users ask questions and receive concise answers. Typical exchanges are 500-1500 words.
Decision Support & Action Plan (1K → 2K): Complex tasks requiring reasoning and analysis. The model receives detailed context and produces comprehensive responses including analysis, recommendations, and actionable plans.
Document Writing Assistant (1K → 2K): Long-form content generation where users provide outlines or context, and the model generates complete documents, articles, or reports.
Concurrency Levels
We tested at 16, 32, and 64 concurrent requests to understand how the system behaves under increasing load. This range covers typical deployment scenarios from small teams to moderate-scale production environments.
Results
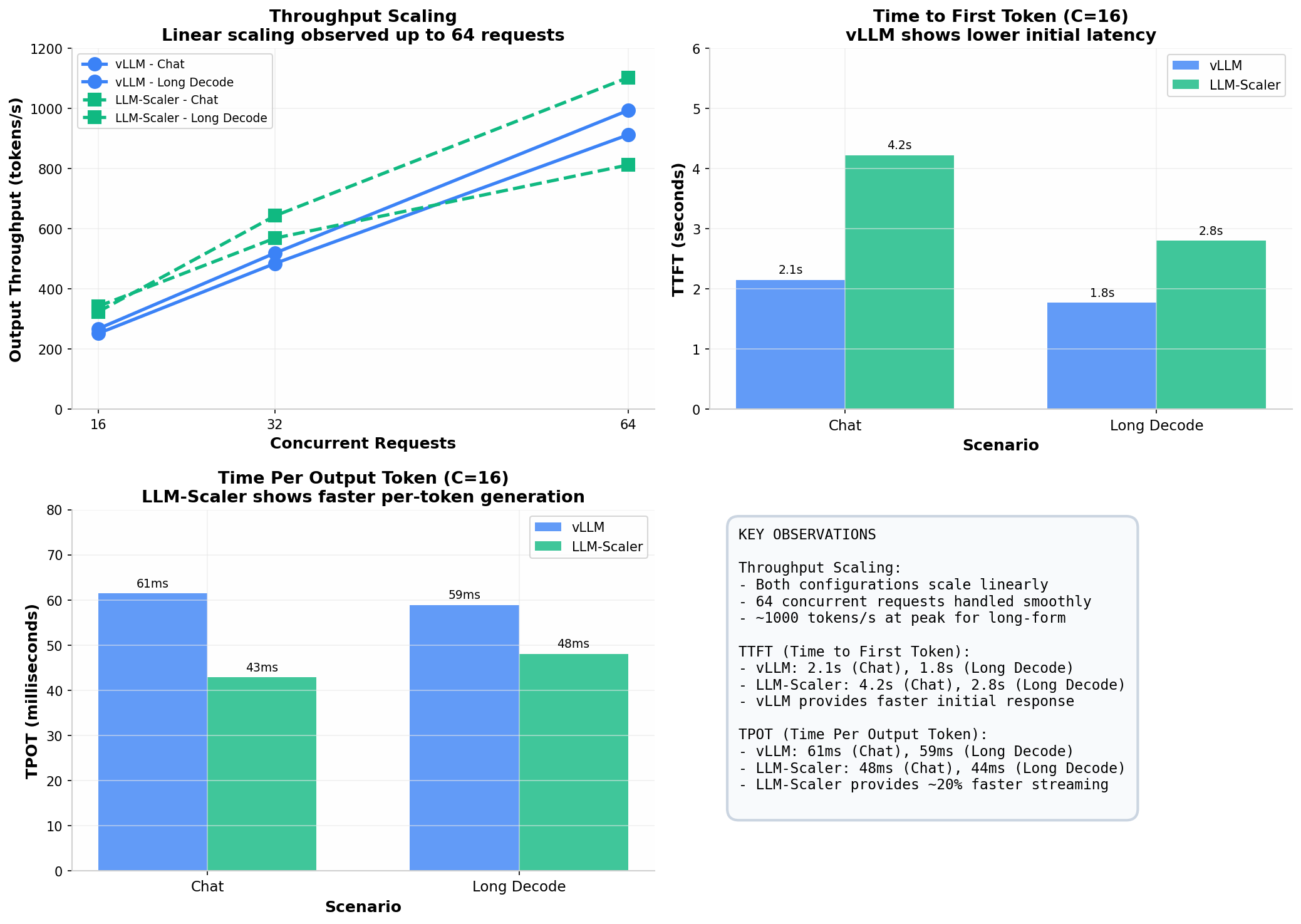 Figure 2: Performance comparison across metrics
Figure 2: Performance comparison across metrics
Throughput Scaling
Both configurations demonstrated linear scaling from 16 to 64 concurrent requests. Throughput approximately doubled when moving from 16 to 32 requests, and doubled again from 32 to 64. This indicates the B60 can handle increased load without significant degradation.
Time to First Token (TTFT)
TTFT measures the latency from request submission to the first token being returned. At 16 concurrent requests:
| Scenario | vLLM | LLM-Scaler |
|---|---|---|
| Chat (1K→1K) | 2.1 seconds | 4.2 seconds |
| Decision Support (1K→2K) | 1.8 seconds | 2.8 seconds |
vLLM consistently shows lower initial latency. This difference is most pronounced in the Chat scenario.
Time Per Output Token (TPOT)
TPOT measures the inter-token latency during generation - effectively how smoothly the output streams to the user. Lower values indicate faster per-token generation. At 16 concurrent requests:
| Scenario | vLLM | LLM-Scaler |
|---|---|---|
| Chat (1K→1K) | 61 ms/token | 48 ms/token |
| Decision Support (1K→2K) | 59 ms/token | 44 ms/token |
The Intel-optimized LLM-Scaler build shows approximately 20-25% improvement in per-token generation time. For long-form content generation, this translates to noticeably faster completion times.
Analysis
Scaling Characteristics
The linear scaling observed up to 64 concurrent requests is noteworthy. This suggests the B60 can serve as the foundation for production deployments handling moderate concurrent load. For context, 64 concurrent users could represent:
- A customer support team of 20-30 agents, each handling 2-3 simultaneous conversations
- An internal AI assistant serving 200 employees with 30-40 concurrent users at peak
- A decision support system with moderate user concurrency
Configuration Trade-offs
The choice between vLLM and the Intel-optimized build involves trade-offs:
| vLLM (Standard Build) | LLM-Scaler (Intel Optimized) |
|---|---|
| Lower TTFT Faster initial response Good for search-like interactions | Lower TPOT Faster token streaming Good for chat-like interactions |
| Example: FAQ bots, quick lookup tools | Example: Writing assistants, decision support systems |
Both builds deliver comparable throughput. The decision depends on which latency metric matters more for your use case.
Conclusions
Based on our testing, the Intel Arc Pro B60 demonstrates viable performance for inference workloads with the following characteristics:
- Serves 50-64 concurrent requests with linear scaling
- Achieves ~1000 tokens/s throughput for long-form generation at peak load
- Provides sub-5 second TTFT for typical workloads
- Benefits from Intel-specific optimizations in the LLM-Scaler build
For organizations evaluating hardware options, the B60 represents a cost-effective entry point for inference deployments. It is not a replacement for high-end NVIDIA hardware in all scenarios, but it offers a practical alternative for moderate-scale production workloads.
The availability of an Intel-optimized vLLM build is a positive development, providing measurable performance improvements without requiring changes to application code.
Acknowledgment
We would like to thank Sparkle for providing the 4x Intel Arc Pro B60 workstation used for this benchmarking. We also thank Chendi Xue from Intel for technical support on vLLM XPU build. Their support made this analysis possible.
Appendix: Technical Details
For reproducibility, the complete test parameters are as follows:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Hardware Provider | Sparkle (https://www.sparkle.com.tw/) |
| GPU Configuration | 4x Intel Arc Pro B60 |
| VRAM | 24GB per GPU |
| Memory Bandwidth | 456 GB/s per GPU |
| Tensor Parallelism | 4 (TP=4 across all GPUs) |
| Model | Qwen/Qwen3-VL-30B-A3B-Instruct |
| vLLM Build | Built from source, v0.12 |
| LLM-Scaler Build | Intel-optimized vLLM, v1.2 |
| Concurrency Levels | 16, 32, 64 |